T
he Federal Reserve Bank of Boston's report on real estate in New England offers valuable insights into the region's housing market. The report, "New England's Housing Markets: Supply and Demand Factors Affecting Housing Prices across the Region," by Sam Shampine, delves into the economic factors driving housing affordability issues.
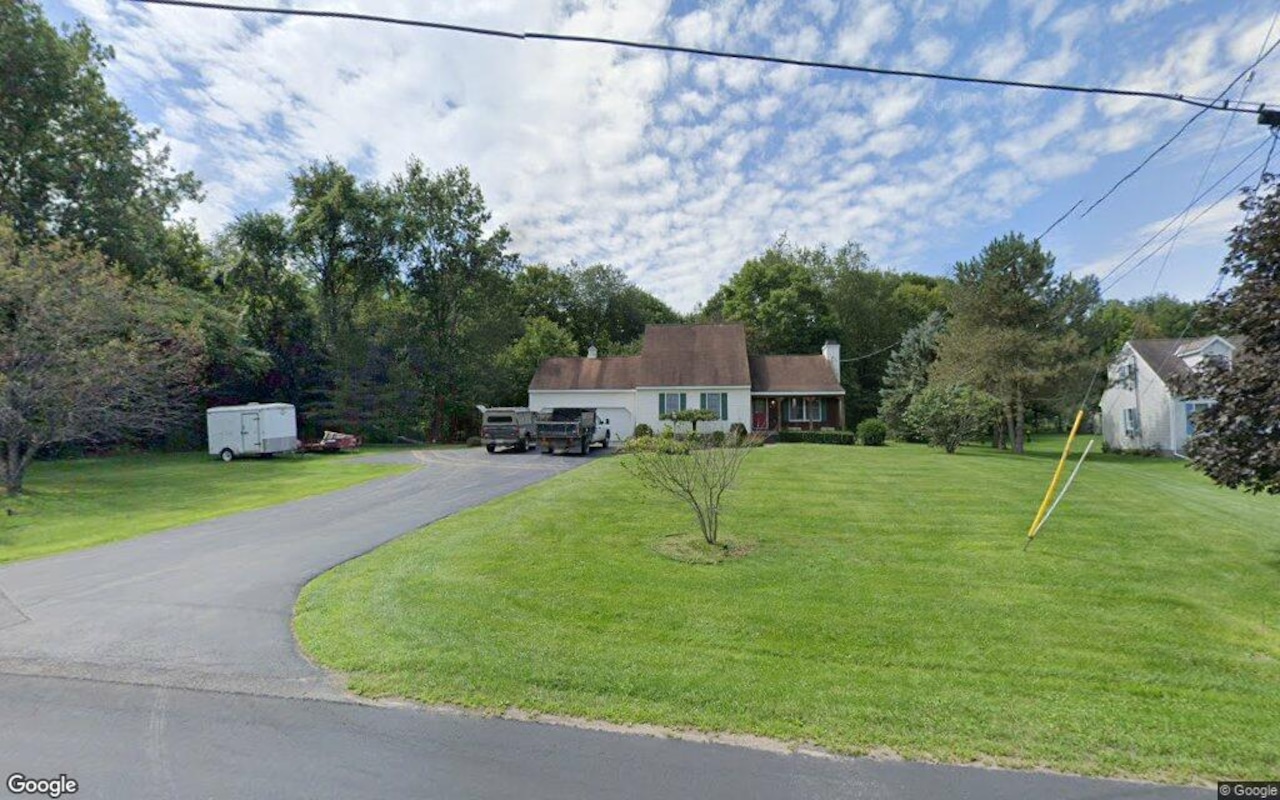
A key takeaway is that Portland stands out as a winner in the region's housing market. However, to understand why, it's essential to consider various factors beyond supply-and-demand imbalances. The report highlights migration, regional differences, and the impact of COVID-19 on the market.
Policymakers aim to alleviate price pressure on housing by increasing supply, but this goal has been elusive. Building permits have increased in New England, but at a rate half the national average. Maine, Connecticut, and Vermont have seen significant growth in permit issuance, while Massachusetts' permits took a sharp decline after the pandemic.
The large metropolitan areas of Boston and Portland have gained more new permits than outlying areas. Boston remains under market stress, whereas Portland has accommodated an increasing share of underserved homebuyers. Multifamily housing permits show a rosier picture, with New England outperforming the national average in Connecticut and Massachusetts.
Migration has brought growth to Maine, New Hampshire, and Connecticut, which have seen higher numbers of new residents. The high permitting rate in Maine is another reason for Portland's success. Meanwhile, Massachusetts and Rhode Island experienced flat population growth, reducing demand pressure on the market.
Real per capita income declined across all six states, but Maine bucked this trend by outperforming the national average. This has contributed to a more favorable housing picture in Maine. The report notes that areas with high income growth tend to issue more permits, attract more migrants, and see rising home values and rents.
The report raises questions about zoning laws' impact on the market. Zoning regulations often hinder housing development, and many homeowners are hesitant to support affordable housing initiatives due to concerns about lowering property values. This sentiment is evident in areas like Boston's suburbs, where residents have resisted zoning changes that could lead to more affordable housing.
However, some regions, such as New England's gateway cities, already have existing zoning laws and vacant industrial structures that can be repurposed for housing. Portland has successfully leveraged this opportunity, demonstrating the potential benefits of redeveloping underutilized areas.